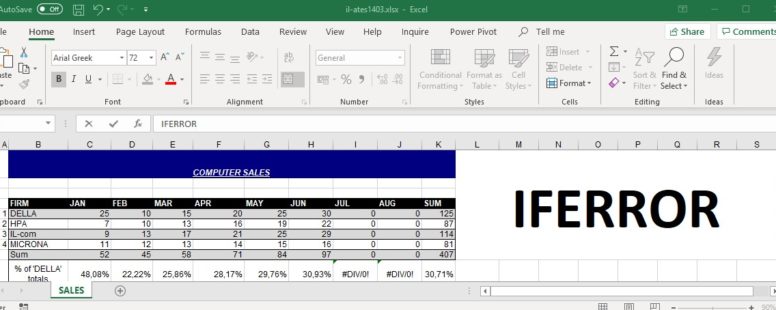
The IFERROR Function
It returns a value you specify if a formula leads to an error. If there is no error in the formula IFERROR returns its result. It is part of the logical functions of Excel.
It returns a value you specify if a formula leads to an error. If there is no error in the formula IFERROR returns its result. It is part of the logical functions of Excel.
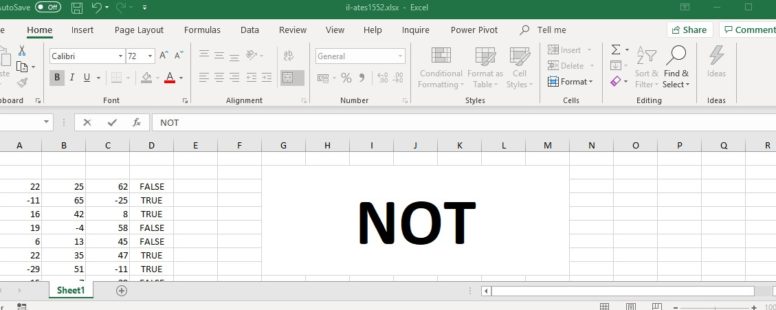
It returns the inverse of a logical value. If a logical value is TRUE it returns FALSE and vice versa. It is part of the logical functions of Excel.
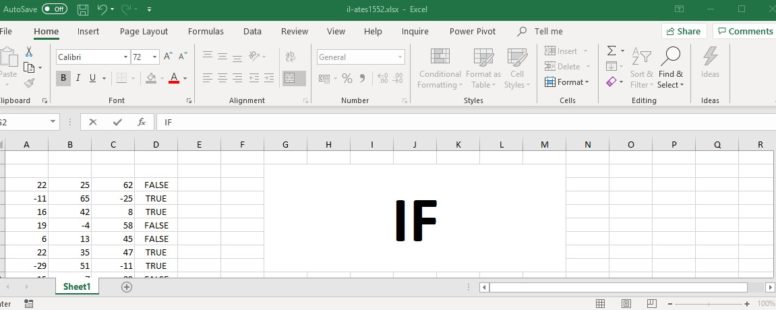
It is used to make logical comparisons between two values and return two results. One if the comparison is TRUE and one if the comparison is FALSE. It is part of the logical functions of Excel.
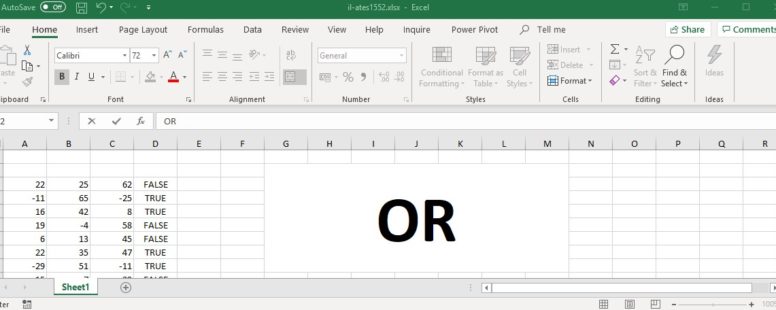
It is used to determine if any of the conditions in its arguments is TRUE. If even one of its arguments is TRUE the function will return TRUE. It is part of the logical functions of Excel.
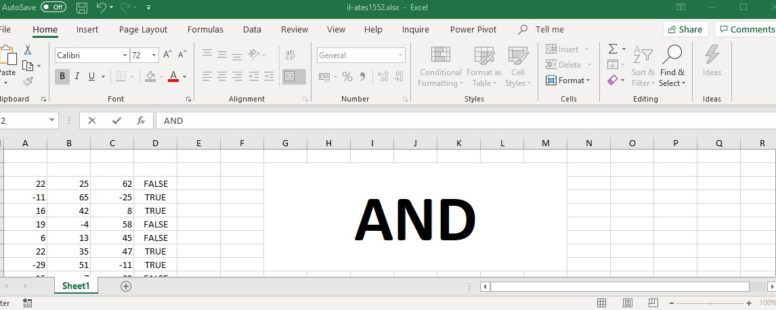
It is used to determine if all the conditions in its arguments are TRUE. If even one of its arguments is FALSE the function will return FALSE. It is part of the logical functions of Excel.
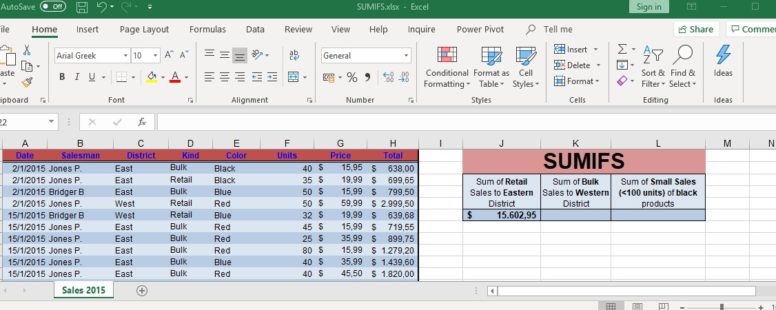
The SUMIFS function adds the cells that meet all its multiple criteria. Even though its logical elements, it is part of the Mathematical functions of Excel.
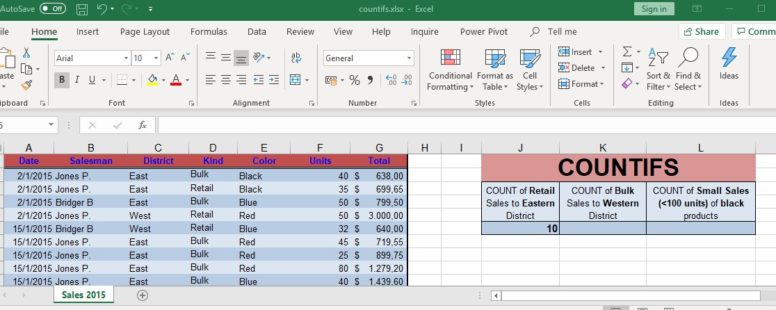
The COUNTIFS function counts the number of times certain criterias are met. Even though its logical elements, it is part of the Statistical functions of Excel.
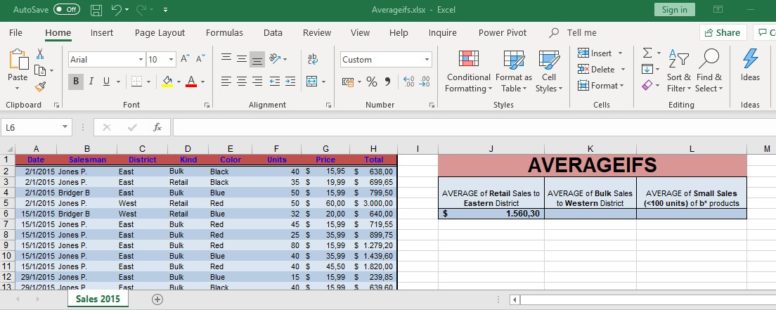
The AVERAGEIFS function returns the arithmetic mean (average) of all the cells that meet all its multiple criteria. Even though its logical elements, it is part of the Statistical functions of Excel.
Excel has provided us with several functions to help us make sense of huge pools of data. SUMIFS is one of them.

Excel has provided us with several functions to help us make sense of huge pools of data. COUNTIFS is one of them.
